- DE
- EN
Modern processes for recycling components and materials are an important part for improving the circularity of products. However, a resource-efficient circular economy requires the cooperation of all stakeholders. For this reason, VDI ZRE's brief analysis no. 33 "Resource efficiency through innovative recycling technologies and processes" provides an insight into the current status of the development of innovative recycling technologies and utilisation processes for plastics, batteries and accumulators, old electrical appliances and precious and special metals as well as PV modules. In addition, SMEs in the processing industry in particular will gain an insight into the processes and current opportunities and challenges the waste disposal and recycling industry are facing currently.
 ©
PantherMedia / Romaset, VDI ZRE
©
PantherMedia / Romaset, VDI ZRECooling lubricants (coolants) are of great importance in metal cutting and forming. They increase the productivity and cost-effectiveness of the processes. In companies in the metalworking industry, water-miscible cooling lubricants are used in around 90 % of machining processes. They consist of a mostly mineral oil-based base oil and an additive package.
 © Kadmy/Fotolia.com
© Kadmy/Fotolia.comThe digital transformation in industrial production offers considerable potential for increasing material and energy efficiency in companies. At the same time, the digitisation technologies used also require resources themselves: materials, including critical raw material, are used in the production of ICT components. Furthermore, the digital transformation can lead to higher energy consumption. The study "Resource efficiency through industry 4.0 - Potentials for SMEs in the manufacturing sector" focuses on this conflict between opportunities and challenges.
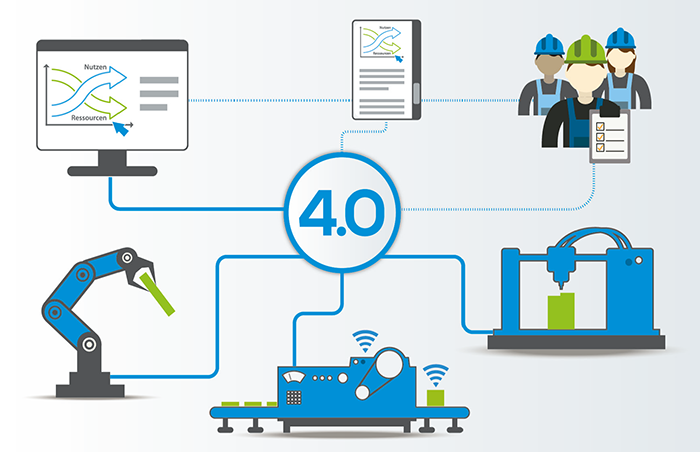 © VDI ZRE
© VDI ZREStationary energy storage systems are a necessary component of a future power supply system with high shares of renewable energies. Used in decentralized industrial applications, they help to increase resource efficiency while minimizing the costs of power supply. Storage solutions for the short to medium-term storage of electrical energy are therefore seen as a contribution to the success of the energy transition being driven forward in Germany.
 © Cybrain/Fotolia.com
© Cybrain/Fotolia.comAdditive processes as a key technology of digitisation are considered to be faster and more cost-effective. Among other things, because less scrap is produced and less waste is generated during manufacturing. Using a specific case study, the study compares the resource consumption of an additive manufacturing process with a conventional manufacturing process.
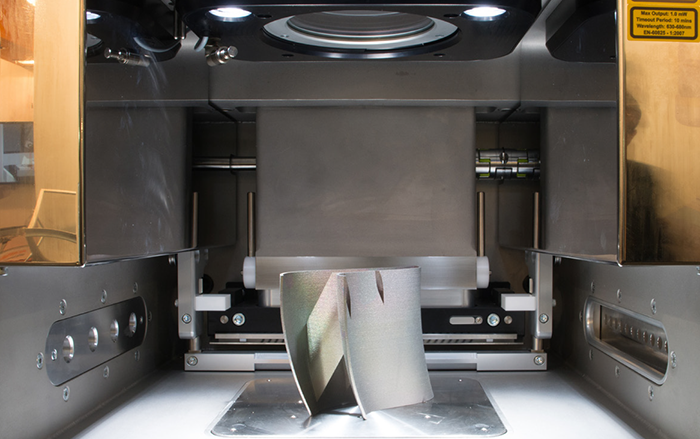 © PantherMedia / moreno.soppelsa
© PantherMedia / moreno.soppelsa