- DE
- EN

Decisions in product development have a significant and direct influence on the use of resources, the environmental impact and the costs incurred along the entire life cycle of products. This clearly demonstrates the ecological and economic responsibility of product development. Around 80 percent of the subsequent environmental impact of the product is determined in the early stages of product development - for example, in the course of defining the product's key features (shape, materials, etc.):
*
McAloone, T. C. und Pigosso, D. C. (2021): Ökodesign - Entwicklung von Produkten mit verbesserter Ökobilanz. In: Bender, B. und Gericke, K., Hg. Pahl/Beitz Konstruktionslehre. Methoden und Anwendung erfolgreicher Produktentwicklung. 9th ed. 2021. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, p. 986.
Second, product development determines about 85 percent of manufacturing costs*
VDI 4800 sheet 1:2016-02: Verein Deutscher Ingenieure e.V., Ressourceneffizienz – Methodische Grundlagen, Prinzipien und Strategien, Berlin: Beuth Verlag GmbH, p. 34.
and between 70 and 80 percent of subsequent product costs (manufacturing costs, operating costs, disposal costs), with their level largely attributable to design decisions.*
Ehrlenspiel, K.; Kiewert, A.; Lindemann, U. und Mörtl, M. (2020): Kostengünstig Entwickeln und Konstruieren - Kostenmanagement bei der Integrierten Produktentwicklung. 8th ed., Berlin/Heidelberg: Springer, p. 15.
*
Ehrlenspiel, K. und Meerkamm, H. (2017): Integrierte Produktentwicklung - Denkabläufe, Methodeneinsatz, Zusammenarbeit. 6th completely revised and expanded edition, München: Hanser, p. 801.
Developing products means finding new solutions to a problem and presenting them as models. The problem is the starting point and trigger for the development and can be, for example, an identified target group need, a product defect that needs to be corrected, competitive pressure, e.g. for increased digital services, or a changed product environment (e.g. environmental protection, increasing scarcity of resources, legal situation).*
Jackstien, K. und Vajna, S. (2014): Grundlagen des Integrated Design Engineering. In: Vajna, S., Ed. Integrated Design Engineering. Ein interdisziplinäres Modell für die ganzheitliche Produktentwicklung. Berlin: Springer Vieweg, p. 72.
In this way, product development is thus viewed as a problem-solving process for which, in addition to rational logical thinking, human creativity enables new ideas and solutions.*
Gericke, K.; Bender, B.; Pahl, G.; Beitz, W.; Feldhusen, J. und Grote, K.-H. (2021): Grundlagen methodischen Vorgehens in der Produktentwicklung. In: Bender, B. und Gericke, K., Hg. Pahl/Beitz Konstruktionslehre. Methoden und Anwendung erfolgreicher Produktentwicklung. 9th ed. 2021. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, p. 40ff.
*
Gericke, K.; Bender, B.; Pahl, G.; Beitz, W.; Feldhusen, J. und Grote, K.-H. (2021): Der Produktentwicklungsprozess. In: Bender, B. und Gericke, K., Hg. Pahl/Beitz Konstruktionslehre. Methoden und Anwendung erfolgreicher Produktentwicklung. 9th ed. 2021. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, p. 61ff.
*
VDI 2221 sheet 1:2019-11: Verein Deutscher Ingenieure e.V., Entwicklung technischer Produkte und Systeme - Modell der Produktentwicklung, Berlin: Beuth Verlag GmbH, p. 22.
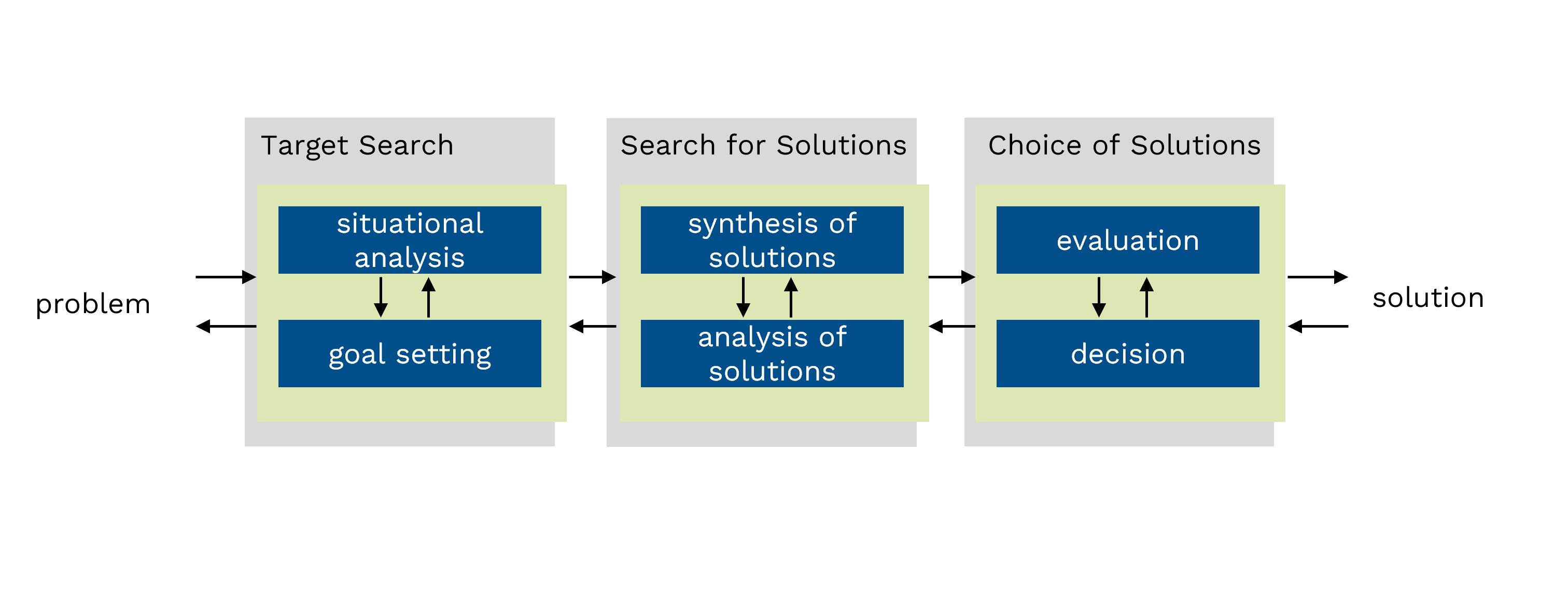 © VDI ZRE (based on VDI 2221 Blatt 1)Product development as a problem-solving process
© VDI ZRE (based on VDI 2221 Blatt 1)Product development as a problem-solving process
Product development represents a fundamental part of the overall product creation process, which also includes product planning and product manufacturing.*
Gericke, K.; Bender, B.; Pahl, G.; Beitz, W.; Feldhusen, J. und Grote, K.-H. (2021): Der Produktentwicklungsprozess. In: Bender, B. und Gericke, K., Hg. Pahl/Beitz Konstruktionslehre. Methoden und Anwendung erfolgreicher Produktentwicklung. 9th ed. 2021. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, p. 59.
Product development takes place as soon as an internal or external development order is received, which at the same time defines the task to be performed by the development department.*
Bender, B. und Gericke, K. (2021): Entwickeln der Anforderungsbasis: Requirements Engineering. In: Bender, B. und Gericke, K., Hg. Pahl/Beitz Konstruktionslehre. Methoden und Anwendung erfolgreicher Produktentwicklung. 9th ed. 2021. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, p. 180.
The result is a product design released for manufacturing with the associated technical product documentation.
Product development follows a general, industry-independent procedure and systematic process that can be divided into four overarching main work phases:
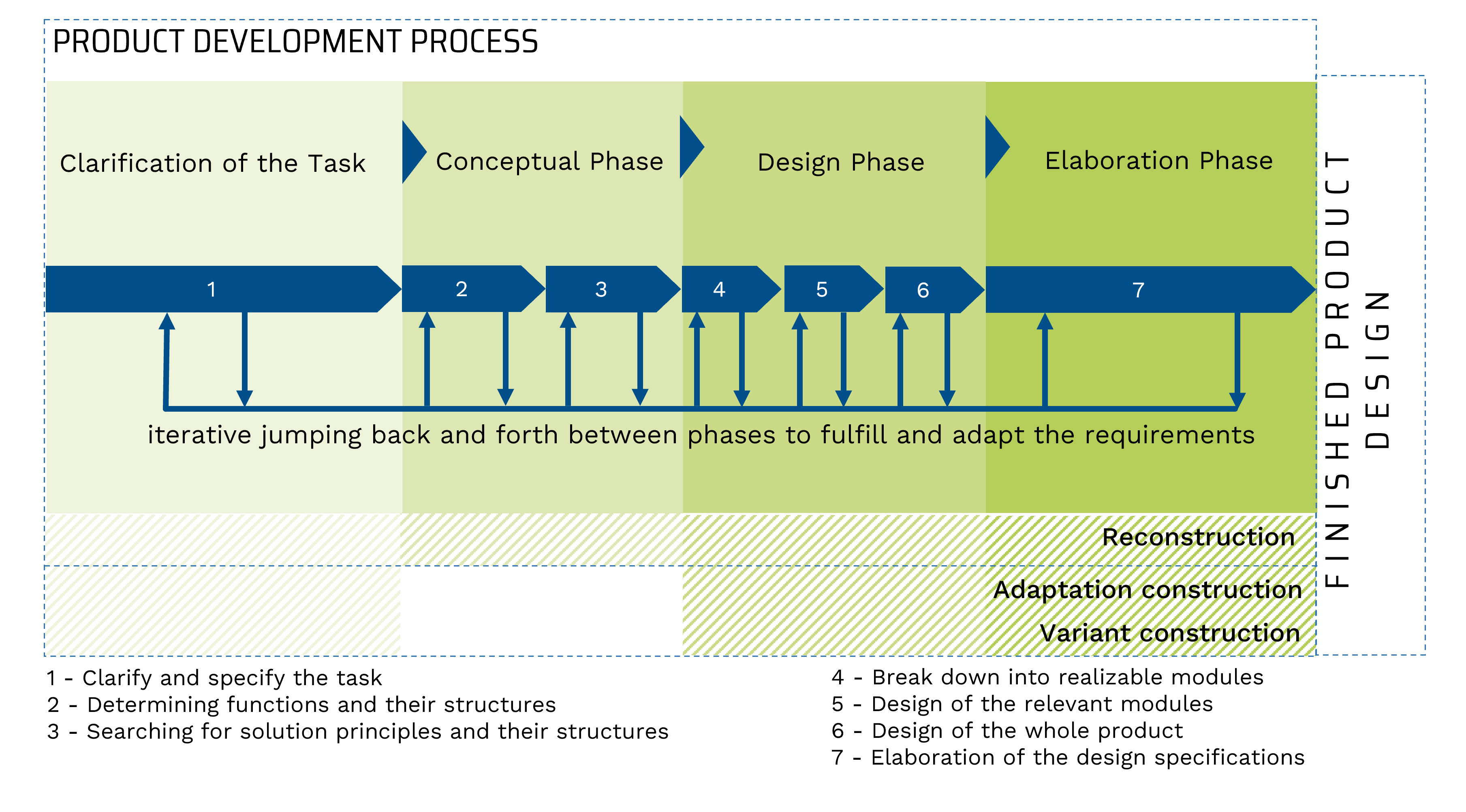 © VDI ZRE
© VDI ZRE
The product development process shown schematically above represents just the core of technical product development. It is also referred to as the process of "developing and designing". However, in this case, the term development stands for a separate division of the company (in addition to production or accounting), while the term design represents a sub-process of development. *
VDI 2221 sheet 1:2019-11: Verein Deutscher Ingenieure e.V., Entwicklung technischer Produkte und Systeme - Modell der Produktentwicklung, Berlin: Beuth Verlag GmbH, p. 27.
*
Ehrlenspiel, K. und Meerkamm, H. (2017): Integrierte Produktentwicklung - Denkabläufe, Methodeneinsatz, Zusammenarbeit. 6th completely revised and expanded edition, München: Hanser Verlag, p. 12.
For successful project execution, other supporting processes accompanying product development are also necessary, either running in parallel or upstream and downstream. The associated interactions between the corresponding corporate areas of product development require cross-departmental coordination, networking and cooperation. *
Gericke, K.; Bender, B.; Pahl, G.; Beitz, W.; Feldhusen, J. und Grote, K.-H. (2021): Der Produktentwicklungsprozess. In: Bender, B. und Gericke, K., Hg. Pahl/Beitz Konstruktionslehre. Methoden und Anwendung erfolgreicher Produktentwicklung. 9th ed. 2021. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, p. 73.
The result is a reduction in development time with lower costs and simultaneously increased product quality.*
Ehrlenspiel, K. und Meerkamm, H. (2017): Integrierte Produktentwicklung - Denkabläufe, Methodeneinsatz, Zusammenarbeit. 6th completely revised and expanded edition, München: Hanser Verlag, p. 236.
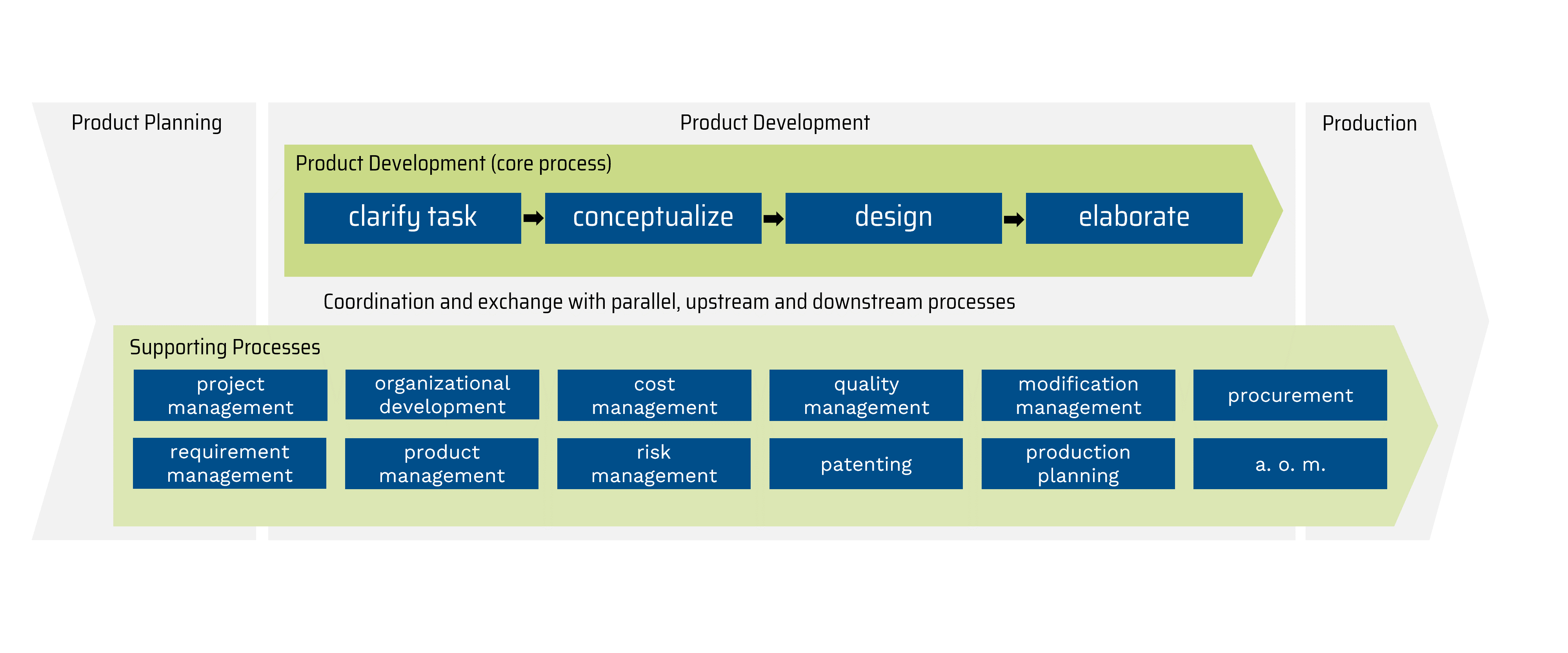 © VDI ZRE based on Gericke et al. (2021)
© VDI ZRE based on Gericke et al. (2021)
Such cross-departmental cooperation, which takes into account the given framework conditions in the company as well as the holistic requirements or needs of all company areas involved in product creation, is summarised under the term integrated product development.*
Gericke, K.; Bender, B.; Pahl, G.; Beitz, W.; Feldhusen, J. und Grote, K.-H. (2021): Der Produktentwicklungsprozess. In: Bender, B. und Gericke, K., Hg. Pahl/Beitz Konstruktionslehre. Methoden und Anwendung erfolgreicher Produktentwicklung. 9th ed. 2021. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, p. 87.
*
Ehrlenspiel, K. und Meerkamm, H. (2017): Integrierte Produktentwicklung - Denkabläufe, Methodeneinsatz, Zusammenarbeit. 6th completely revised and expanded edition, München: Hanser Verlag, p. 9.
During development, decisions and compromises are continuously made to create solutions. Taking into account the various requirements and needs of different stakeholders along the entire value chain, as well as those of the developing company itself, is a fundamental precondition for the market success and sustainability of a product, especially in the case of complex technical products, and requires expertise from different disciplines.
Possible requirements of internal and external stakeholders for a product can be:
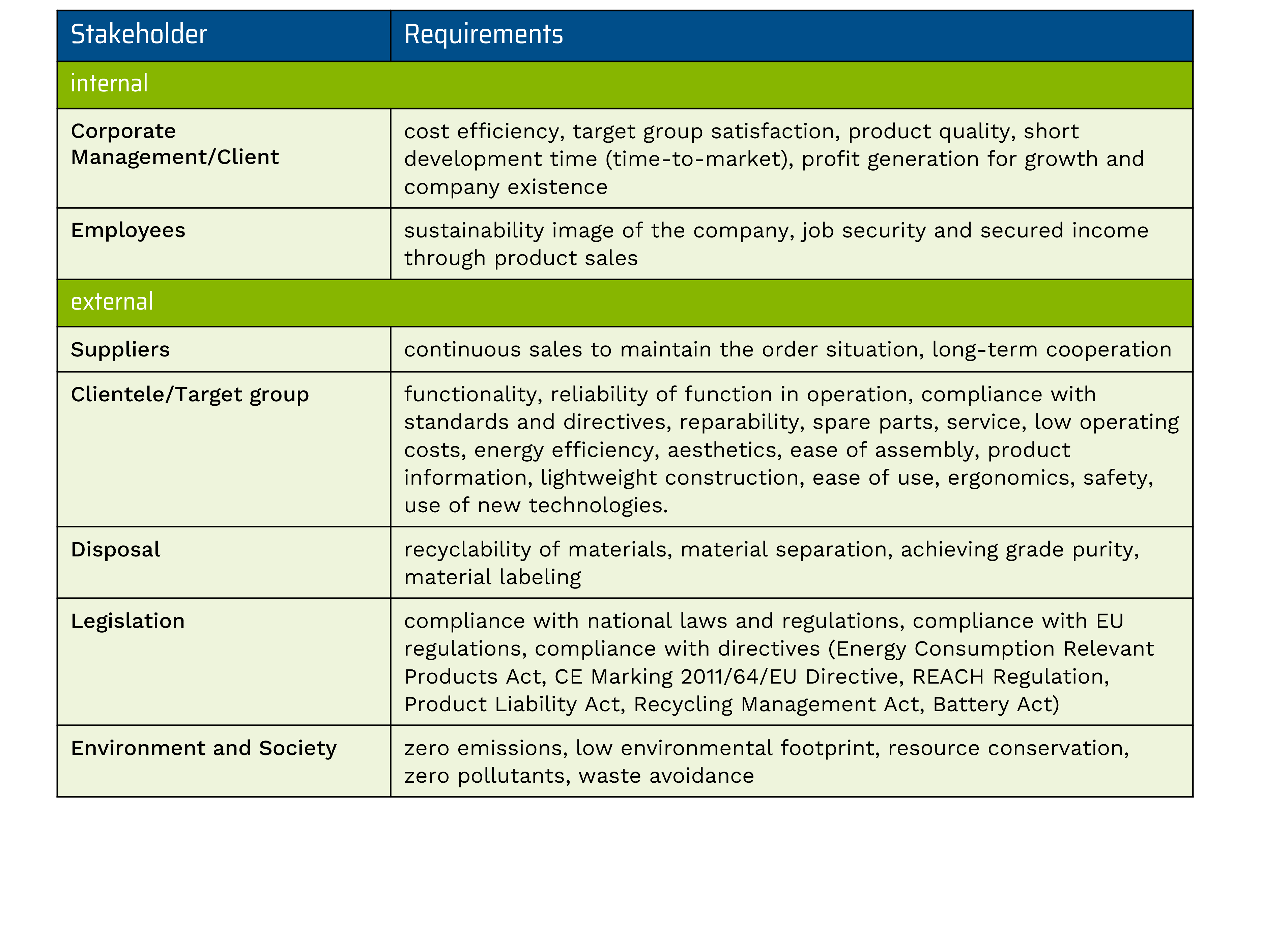 © VDI ZRE
© VDI ZRE
Resource-efficient product development means designing products in such a way that the use of natural resources is kept to a minimum throughout the entire product life cycle, but without compromising functionality or utility.
The development of resource-efficient products thus follows the principles of sustainable development. These state, among other things, that natural resources should be used and consumed as sparingly and with as few emissions as possible so that they are also available to future generations to cover their needs. In addition, their use must not endanger the ecological balance, but rather ensure the further regeneration of ecosystems.*
United Nations (1987): Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development - Our Common Future.
Resource-efficient product development requires a holistic view - both along the entire product life cycle and the product life path. It is generally true that the results of product development depend on and are influenced by the requirements of the respective life cycle phases and actors. This in turn means that every definition of product properties (function, design, material, operating principle, characteristics) and processes (production, disposal) influences the subsequent life cycle process.*
VDI 4800 sheet 1:2016-02: Verein Deutscher Ingenieure e.V., Ressourceneffizienz – Methodische Grundlagen, Prinzipien und Strategien, Berlin: Beuth Verlag GmbH, p. 33f.
These specifications determine, among other things, the use of resources and the environmental impact of the product in the various life cycle phases. To minimisze these impacts, they must be considered, analysed, simulated and evaluated in their entirety in order to draw conclusions for the development of the product.*
Anderl, R. und Melk, K. (2005): Introduction. In: Abele, E.; Anderl, R. und Birkhofer, H., Ed. Environmentally-Friendly Product Development. Methods and Tools. London: Springer, p. 5.
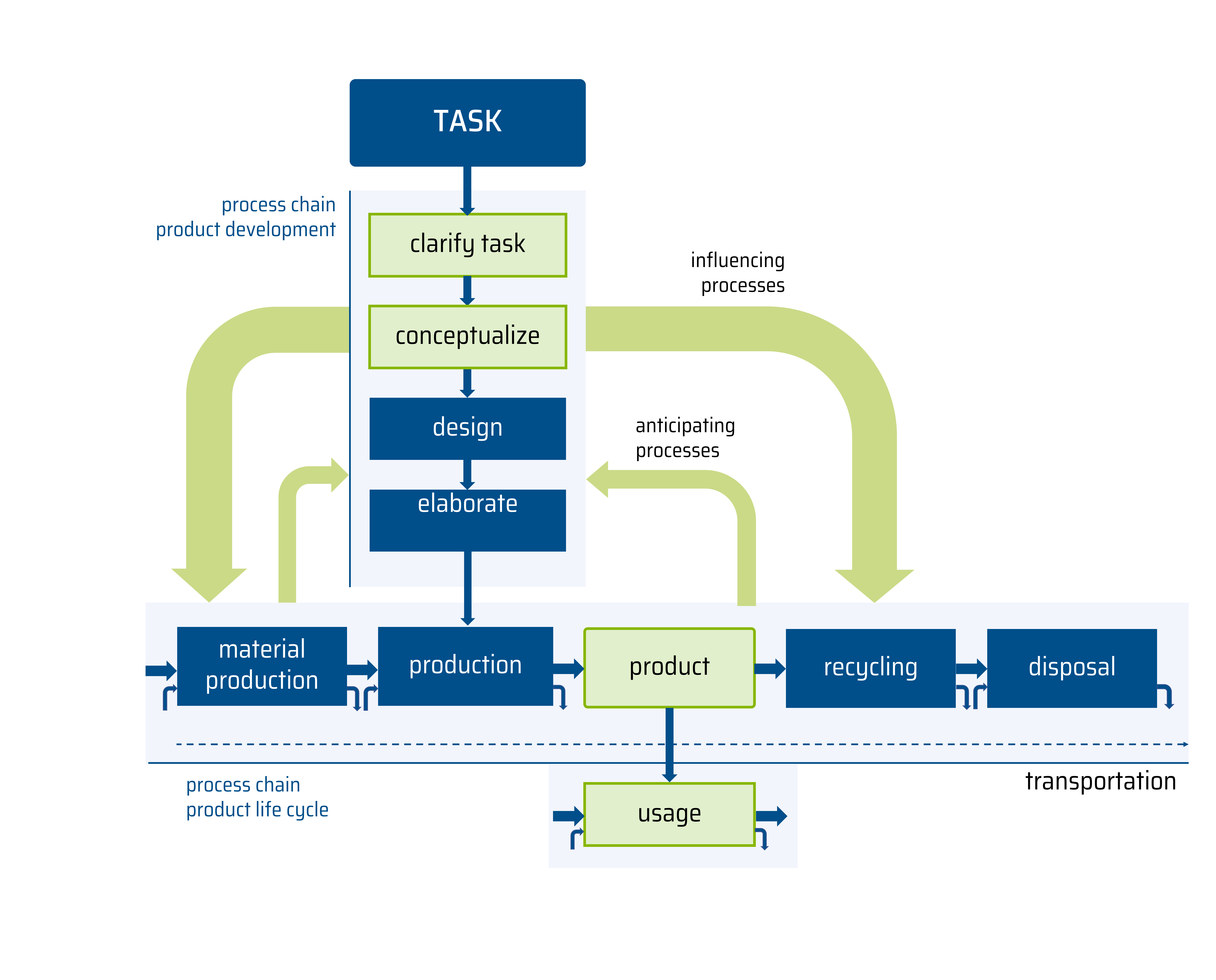 © VDI ZRE
© VDI ZRE
Each stage of product development, with its decisions on product properties, design and manufacturing processes, influences the use of resources as well as environmental impacts and costs. It is essential to integrate and apply resource efficiency strategies and measures as well as process-related and life cycle methods in product development in a targeted manner. Only then can resource efficiency decisions be made in every stage of product development. In this context, decisions in the early phases "clarify task" and "design" sometimes have the greatest influence.*
VDI 4800 sheet 1:2016-02: Verein Deutscher Ingenieure e.V., Ressourceneffizienz – Methodische Grundlagen, Prinzipien und Strategien, Berlin: Beuth Verlag GmbH, p. 34.
To evaluate the ecological and economic consequences of decisions made during product development and to allow any adjustments to be made to subresults, it is necessary to assess resource efficiency throughout the entire life cycle. Depending on the method selected, an evaluation can qualitatively or quantitatively record the expected resource consumption, resulting waste or potential environmental impacts.
Ecodesign is an approach to sustainable and lifecycle-oriented product development that aims to improve the environmental performance of an existing or newly developed product over its entire lifecycle or to minimise the sum of negative environmental impacts.*
McAloone, T. C.; Pigosso, D.C.A. (2021): Ökodesign. Entwicklung von Produkten mit verbesserter Ökobilanz. In: Bender, B. und Gericke, K. (Hg.): Pahl/Beitz Konstruktionslehre. Methoden und Anwendung erfolgreicher Produktentwicklung. 9th ed. 2021. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer (Springer eBook Collection), pp. 975–1021, p. 985f.
By using well thought-out environmentally compatible product design, the following are achieved:
*
van Doorsselaer, K.; Koopmans, R.J. (2021): Ecodesign. A Life Cycle Approach for a Sustainable Future. München: Carl Hanser Verlag, p. 35ff.
With regard to the development of resource-efficient products, the ecodesign methodology thus offers a significant instrument for reducing the product's use of resources through ecological design.
Any use of natural resources is accompanied by the release of emissions and causes environmental damage.*
Ökopol; IDZ: Ecodesign Kit. Einleitung Ökodesignprinzipien. Published by BMU und UBA (accessed on: 07/19/2022).
*
McAloone, T. C.; Pigosso, D. C.A. (2021): Ökodesign. Entwicklung von Produkten mit verbesserter Ökobilanz. In: Bender, B. und Gericke, K. (Hg.): Pahl/Beitz Konstruktionslehre. Methoden und Anwendung erfolgreicher Produktentwicklung. 9th ed. 2021. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, p. 975-1021, p. 984.
Environmental damage refers to changes in the environment that can be attributed in whole or in part to the product during its life cycle and cause environmental problems. They are triggered by the input and output flows in the life phases, for example in the form of used energy, raw materials and auxiliary materials (e.g. adhesives, paints, screws, packaging) as well as outgoing emissions (e.g. pollutants, dusts, dissipations) and non-recyclable wastes.*
van Doorsselaer, K.; Koopmans, R. J. (2021): Ecodesign. A Life Cycle Approach for a Sustainable Future. München: Carl Hanser Verlag (Hanser eLibrary), p. 36.
The environmental problems can be divided into various so-called impact categories, which at the same time form the basis for describing the results of life cycle assessments (see figure below).*
McAloone, T. C.; Pigosso, D. C.A. (2021): Ökodesign. Entwicklung von Produkten mit verbesserter Ökobilanz. In: Bender, B.; Gericke, K. (Ed.): Pahl/Beitz Konstruktionslehre. Methoden und Anwendung erfolgreicher Produktentwicklung. 9th ed. 2021. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, p. 975-1021, p. 983.
The categorisation is not standardised and differs in the various life cycle assessment methods.*
van Doorsselaer, K.; Koopmans, R. J. (2021): Ecodesign. A Life Cycle Approach for a Sustainable Future. München: Carl Hanser Verlag (Hanser eLibrary), p. 109.
Further information on the impact categories can be found in the Ecodesign Kit, published by the Federal Environment Agency.
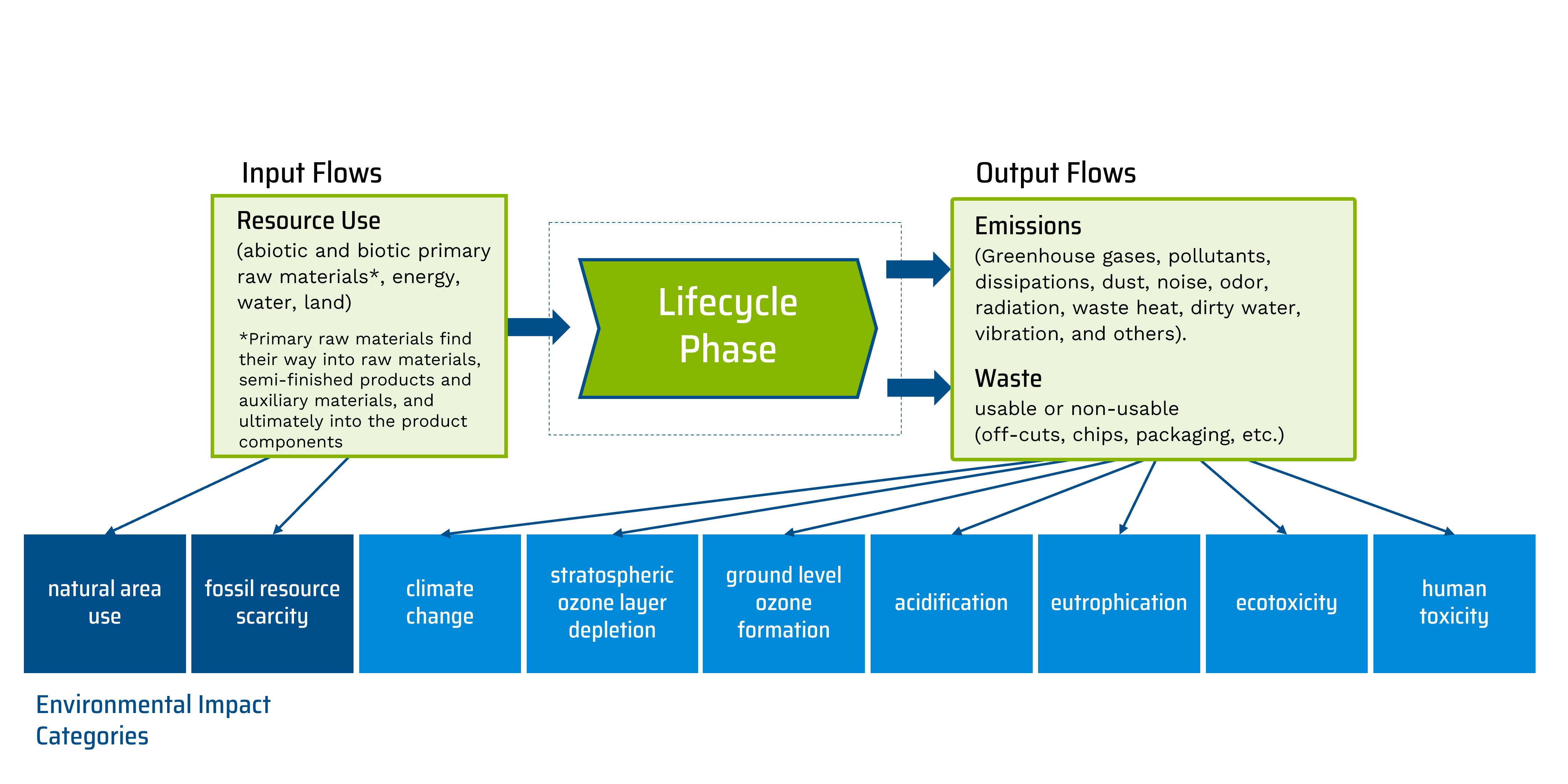 © VDI ZRE
© VDI ZRE
Ecodesign defines various principles as requirements or "simple truths" of environmentally friendly product design.*
Ökopol; IDZ: Ecodesign Kit. Einleitung Ökodesignprinzipien. Published by BMU und UBA (accessed on: 07/19/2022).
Their consideration in product development and application in the design phase is equally target-oriented for the resource efficiency of the product. Neglecting technical and economic requirements is by no means intended; on the contrary, ecological aspects are added to the requirements without neglecting the interests of the stakeholders.
Find out how you can reduce material losses caused by rework in production, for example, and lower your overall energy consumption. Once you have answered all the questions, the evaluation will show you possible efficiency potential in your company. In addition, you will be presented with measures, methods and tools that you can use to reduce resource consumption.
Continue to Resource CheckFind out how you can reduce material losses caused by rework in production, for example, and lower your overall energy consumption. Once you have answered all the questions, the evaluation will show you possible efficiency potential in your company. In addition, you will be presented with measures, methods and tools that you can use to reduce resource consumption.
Continue to Resource CheckGet in touch for further information or help regarding the topic of "Product Development".
Tel.: +49 (0)30 2759506-505
E-Mail: zre-industrie@vdi.de