- DE
- EN
Resource efficiency measures can be implemented at various points in the production process. The potentials are manifold. However, the increasingly complex networked production economy no longer requires only selective but also comprehensive resource efficiency measures, those that work across processes as well as across company and business boundaries.
 © nongkran_ch/Fotolia.com
© nongkran_ch/Fotolia.com
The efficient use of energy, materials, water and space not only saves resources, but also costs for the purchase and disposal of waste, residual materials and wastewater, for example. The networking of companies in an industrial park or with the surrounding residential areas offers many opportunities to save resources. Residential areas in particular offer high efficiency potentials as heat consumers.
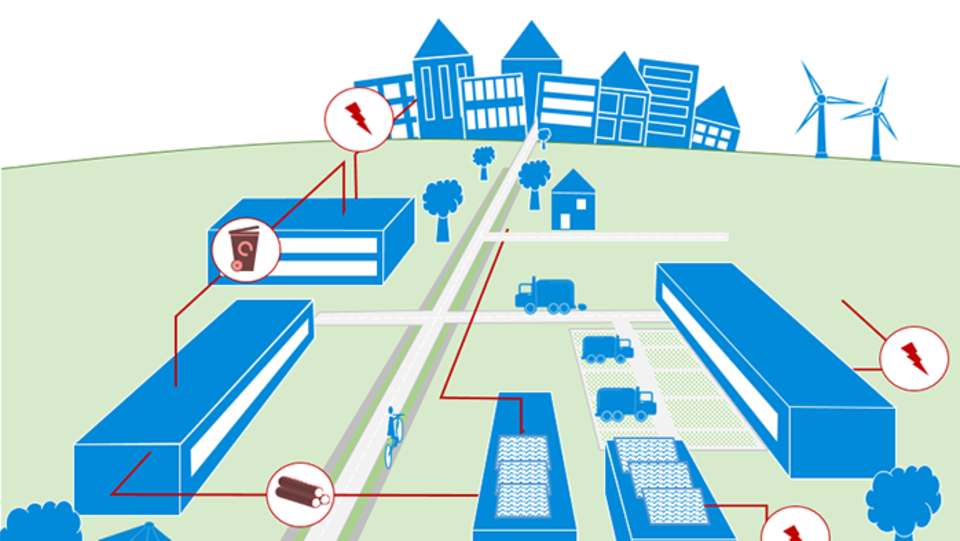 © VDI ZRE
© VDI ZRE
The brochure Competetive Advantage: Resource Efficiency gives an introduction into the meaning of resource efficiency and its strategic and economic advantages.
 © maxmann/Pixabay, sarikhani/Fotolia.com, Indigo/Fotolia.com, WS-Design/Fotolia.com (v.l.n.r.)
© maxmann/Pixabay, sarikhani/Fotolia.com, Indigo/Fotolia.com, WS-Design/Fotolia.com (v.l.n.r.)
Stationary energy storage systems are a necessary component of a future power supply system with high shares of renewable energies. Used in decentralized industrial applications, they help to increase resource efficiency while minimizing the costs of power supply. Storage solutions for the short to medium-term storage of electrical energy are therefore seen as a contribution to the success of the energy transition being driven forward in Germany.
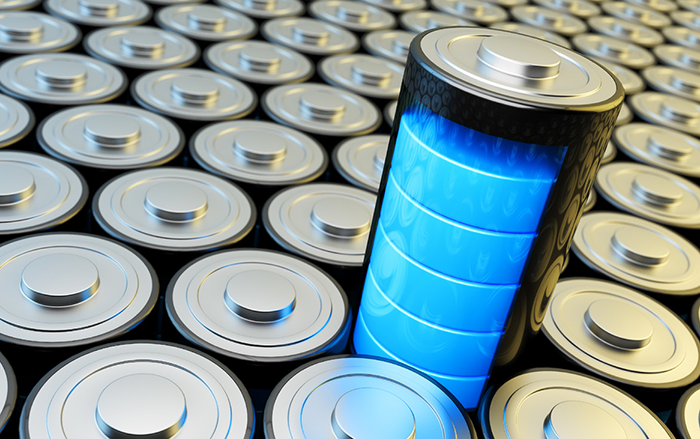 © Cybrain/Fotolia.com
© Cybrain/Fotolia.com
Product development has a fundamental influence on the resource efficiency of a product. Resource-conscious and forward-looking product development can significantly influence the use of materials and consequently the cost expenditure along the entire product life cycle. With regard to finite re-sources, it should be a pillar of the strategic orientation of the business.
 © Jennewein Photo/Fotolia.com
© Jennewein Photo/Fotolia.com
Biomimetics combines biology and technology in an interdisciplinary collaboration. It is an interdisciplinary field that is not limited to a research or industrial sector. The aim of biomimetics is to solve technical problems by abstraction, transfer and application of knowledge gained from biological models. Their application in the product development process as innovation method enables innovative technical solutions. These can give companies competitive advantages.
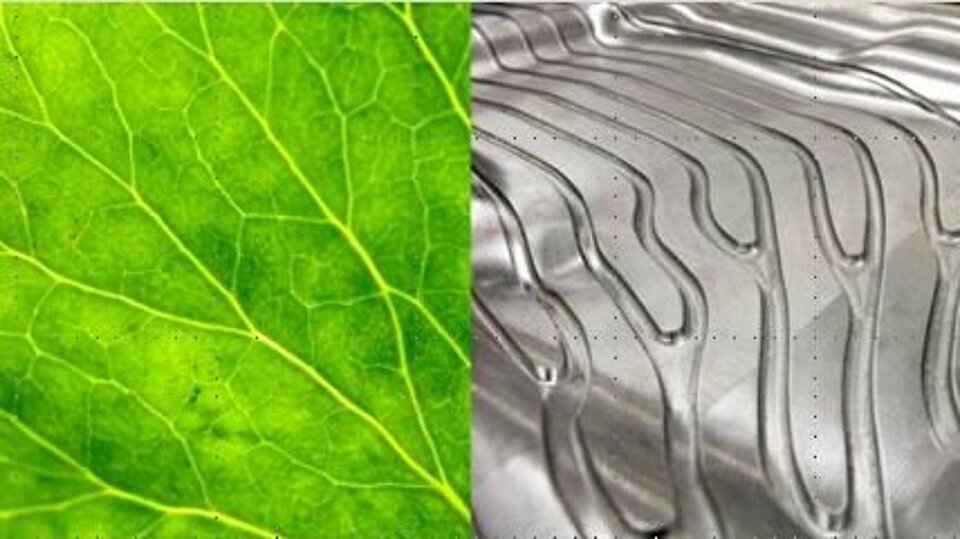 © Ulrich Grunewald
© Ulrich Grunewald
Remanufacturing is a central measure for increasing resource efficiency. The material and energy expenditure for the manufacture of a product and the associated costs are lowered. Through remanufacturing the original high level of value added is retained and the dependence on import of critical raw materials is reduced. Remanufacturing as a key component of a circular economy is viewed as being the preferred option for closing material loops, particularly compared with recycling, and possesses a high resource efficiency potential.
 © Tomasz Zajda/Fotolia.com
© Tomasz Zajda/Fotolia.com
Cooling lubricants (coolants) are of great importance in metal cutting and forming. They increase the productivity and cost-effectiveness of the processes. In companies in the metalworking industry, water-miscible cooling lubricants are used in around 90 % of machining processes. They consist of a mostly mineral oil-based base oil and an additive package.
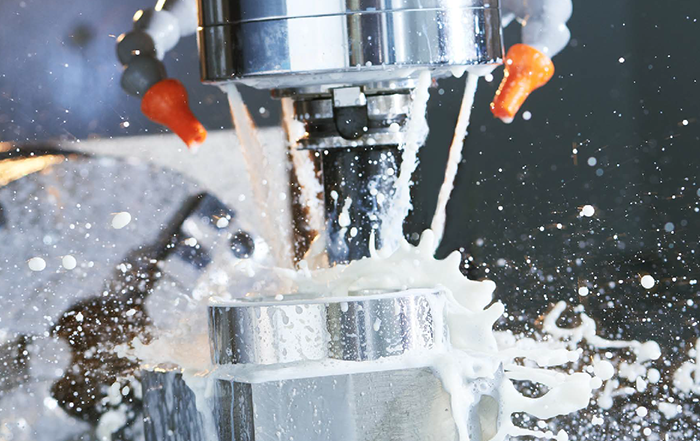 © Kadmy/Fotolia.com
© Kadmy/Fotolia.com
The digital transformation in industrial production offers considerable potential for increasing material and energy efficiency in companies. At the same time, the digitisation technologies used also require resources themselves: materials, including critical raw material, are used in the production of ICT components. Furthermore, the digital transformation can lead to higher energy consumption. The study "Resource efficiency through industry 4.0 - Potentials for SMEs in the manufacturing sector" focuses on this conflict between opportunities and challenges.
 © VDI ZRE
© VDI ZRE
Lightweight construction is a prime example of demonstrating the potential of resource efficiency. Resource efficiency potentials in the utilisation phase of mobile products have already been investigated frequently and are widely known. In addition, the various lightweight engineering strategies and materials also offer opportunities for increasing resource efficiency in the production phase and in recycling and disposal.
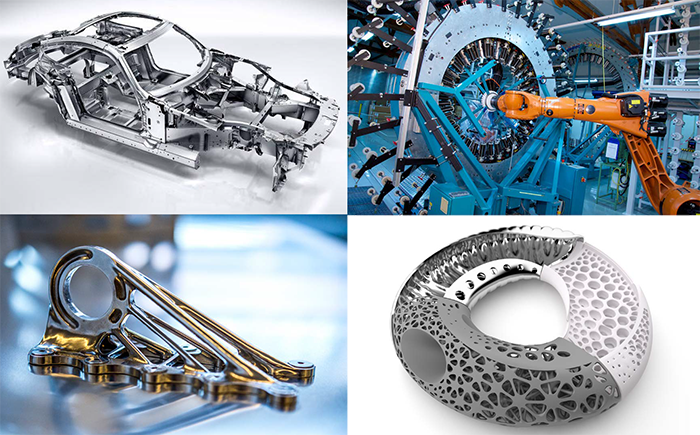 © Space Frame des Mercedes-AMG GT
© Space Frame des Mercedes-AMG GT
You got questions or need further information?
We look forward to hearing from you! Feel free to get in touch with your request or suggestion.