- DE
- EN
There is a multitude of methods and tools that exist for different questions and problems and can be applied for the implementation of resource efficiency in the business. The Resource Efficiency Guide helps you to tackle resource efficiency measures in your business step by step and helps you to find the right method or tool for each step.
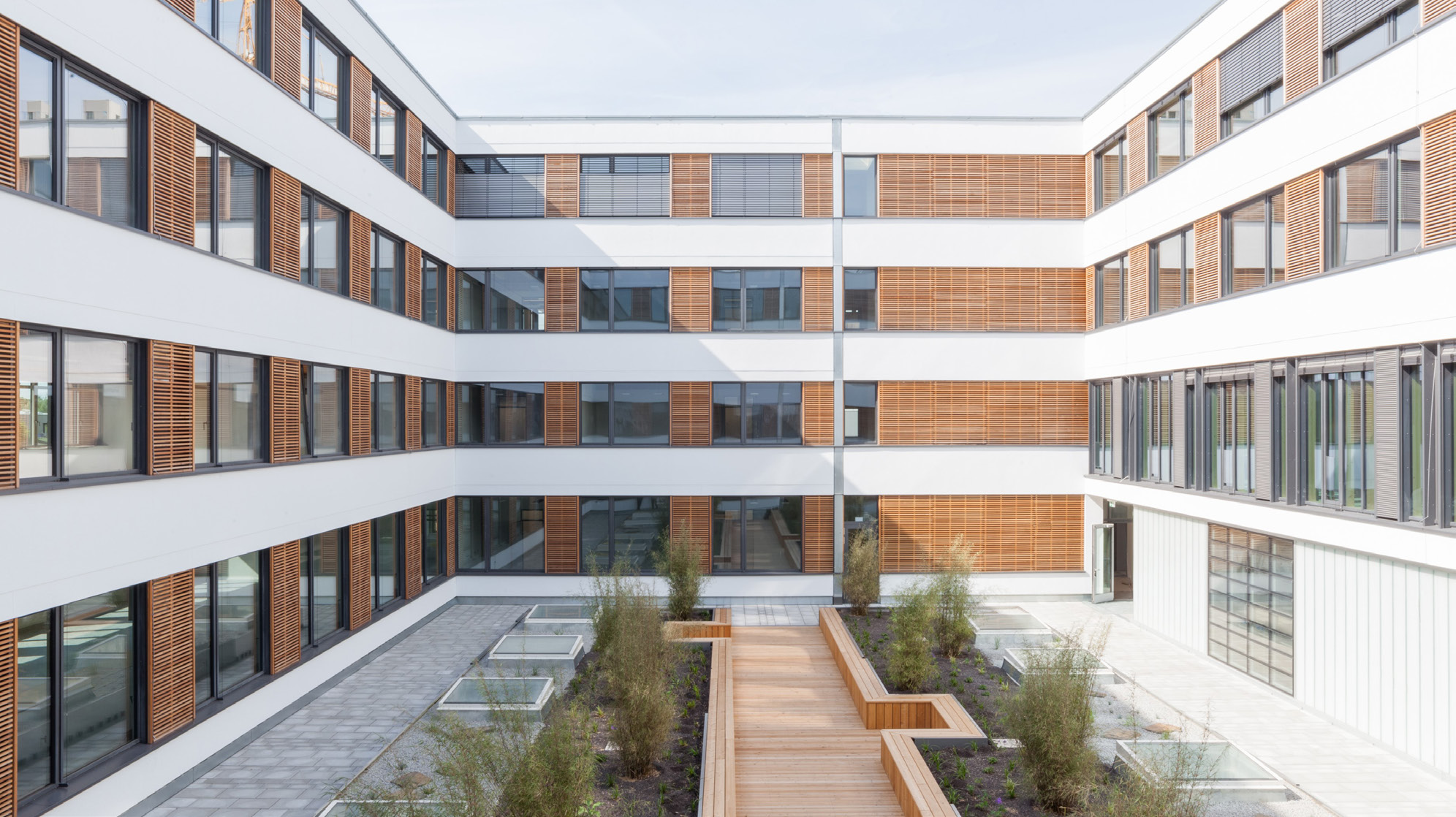
The course for the most efficient use of natural resources is already set in the early planning phases of a building. With the help of Building Information Modelling (BIM), the entire planning process can be optimised and the use of natural resources minimised.
 © kister scheithauer gross architekten und stadtplaner GmbH
© kister scheithauer gross architekten und stadtplaner GmbH
The ESTEM final report contains results of the environmental analysis, discussions in workshops with the professional public, information concerning the actual development of methods and particular case studies. The final report is supplemented by the Excel®-based ESTEM tool and an associated guideline.
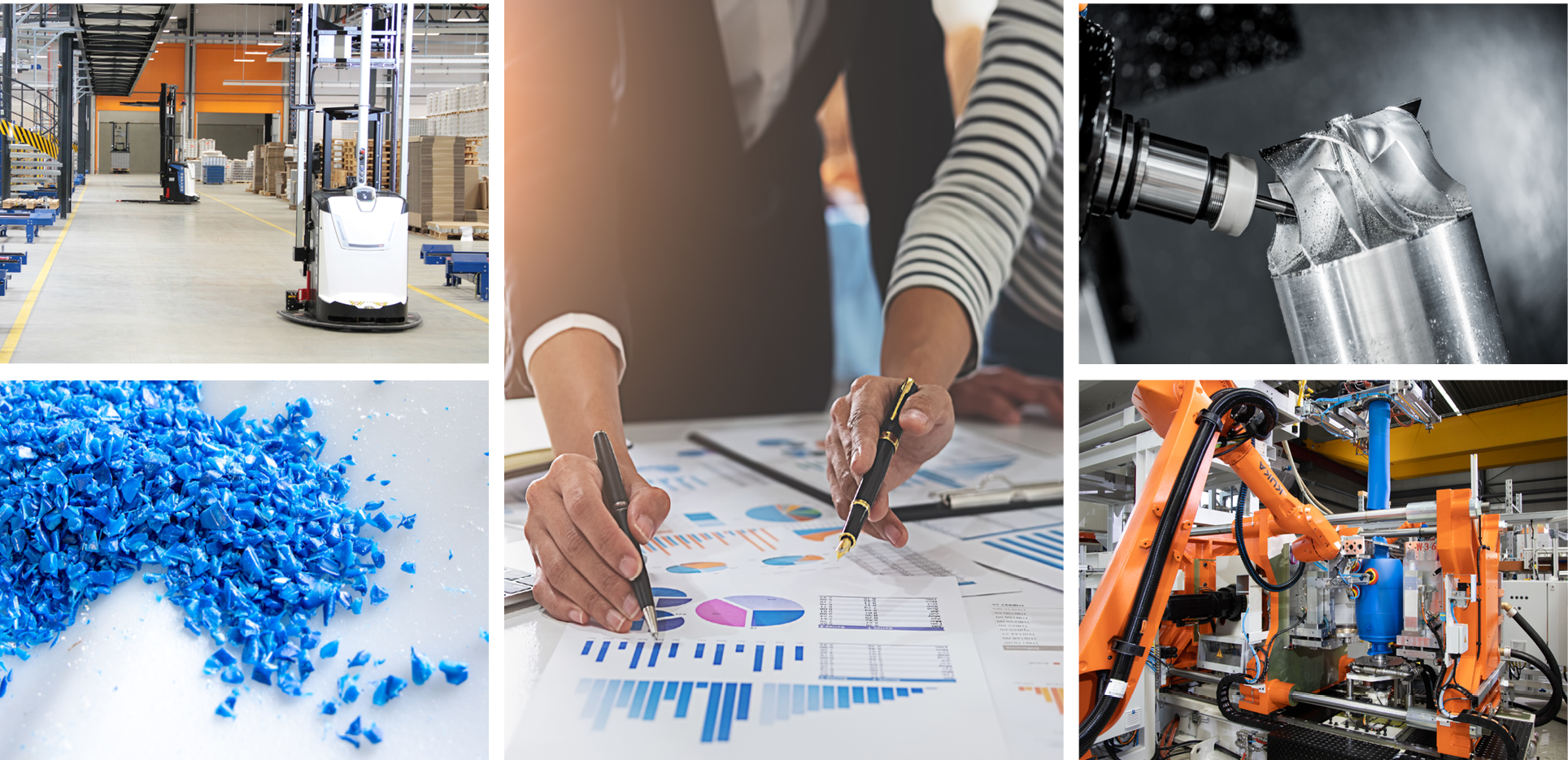 © VDI ZRE, AdobeStock/MIND AND I, PantherMedia/cookelmar, VDI ZRE, VDI ZRE
© VDI ZRE, AdobeStock/MIND AND I, PantherMedia/cookelmar, VDI ZRE, VDI ZRE
The brochure provides an overview of the definition of resource efficiency and options for integrating resource efficiency aspects from planning to construction. It contains further information and helpful tools as well as best practices.
 © ZRS Architekten
© ZRS Architekten
Modern processes for recycling components and materials are an important block for improving the circularity of products. This brief analysis by VDI ZRE now presents new technologies for a resource-efficient circular economy.
 © PantherMedia / Romaset, VDI ZRE
© PantherMedia / Romaset, VDI ZRE
By digitally recording, storing and integrating resource data, material and energy consumption can be tracked and reduced. This is due to the effect that digital approach makes potential savings quantifiable. However, the value of this data is often difficult to grasp for SMEs.
 © PantherMedia / Gorodenkoff, VDI ZRE
© PantherMedia / Gorodenkoff, VDI ZRE
Via simulation instead of prototypes: Digital technologies simplify the development of products and services in many ways. Simultaneously, companies face the challenge of dealing with the complexity of data management. The following brief analysis "Digital technologies for the development of resource-efficient products and services" points out how companies can save natural resources already in product development through digitisation, "Industrie 4.0" and innovative methods.
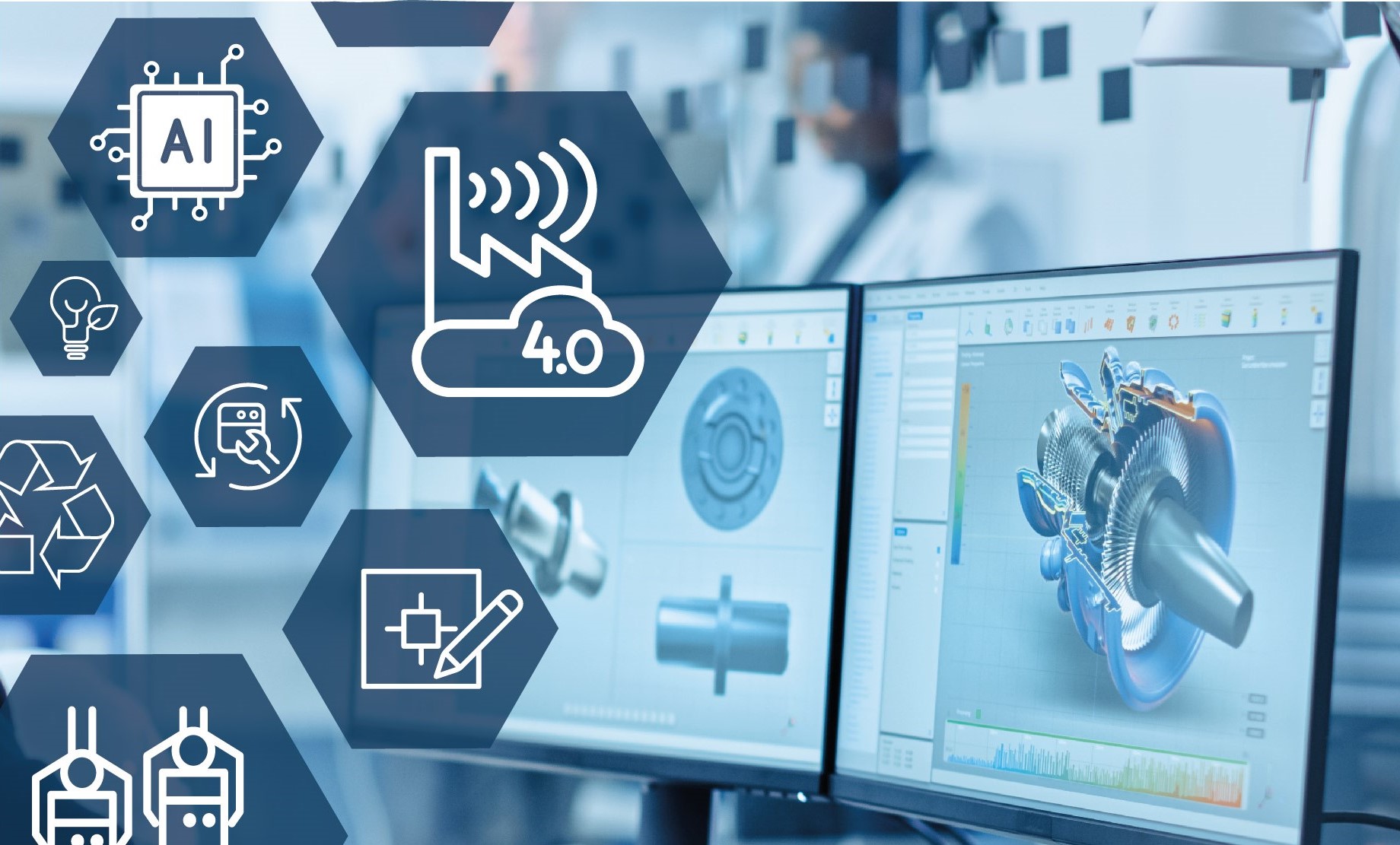 © PantherMedia/Gorodenkoff (edited)
© PantherMedia/Gorodenkoff (edited)
The concept of a lean, holistic production system – with the essential goal of avoiding waste – has been known since the early 1990s. The reason is that a holistic approach reveals numerous savings potentials for material and energy as well as possible strategies for increasing resource efficiency in companies. The brief analysis "Resource efficiency via production planning and Lean Production" therefore provides an overview of which production methods SMEs can use to save material and energy and thus act more resource-efficiently.
 © PantherMedia / nikkytok, VDI ZRE
© PantherMedia / nikkytok, VDI ZRE
The worlds of business and industry have undergone some significant changes in recent years. Established institutions are being supplanted by competitors with completely new business models. Online lexicons are replacing encyclopaedias, the largest accommodation platform doesn’t own a single one of the properties it offers. New competitors with innovative business ideas are surging into the market, largely as a result of digitisation. Alongside the challenges of a world that continues to change at an ever-faster rate, these developments can present far-reaching opportunities when it comes to industry and resource efficiency.
 © PantherMedia / trueffelpix
© PantherMedia / trueffelpix
Both the retail and logistics sectors consume large quantities of natural resources, especially raw materials and energy. The transport of goods plays a significant role in this, but so do other factors such as the construction and operation of retail. The aim of this brief analysis is to provide companies in the retail and logistics sectors with suggestions for resourceefficient business process design. The strategies, measures and practical examples presented here are also intended to help tap additional potential in terms of resource efficiency.
 © PantherMedia / perig76
© PantherMedia / perig76
Cleanliness requirements and the associated residual dirt specifications have risen sharply in the area of industrial parts manufacturing in recent years. This is forcing companies to no longer view the cleaning process as a low-priority component of the production chain, but rather as a value-adding processing step. Here, resource efficiency potentials can be tapped, which reduce material and energy and at the same time lead to cost savings.
 © PantherMedia / robertsrob
© PantherMedia / robertsrob
Additive processes as a key technology of digitisation are considered to be faster and more cost-effective. Among other things, because less scrap is produced and less waste is generated during manufacturing. Using a specific case study, the study compares the resource consumption of an additive manufacturing process with a conventional manufacturing process.
 © PantherMedia / moreno.soppelsa
© PantherMedia / moreno.soppelsa
More than half of the total German waste volume is accounted for by construction and demolition waste from the building industry. This is reason enough to include the demolition and dismantling of buildings in the planning of a building from the very beginning, in order to reduce the volume of waste and conserve natural resources. The brief analysis shows the current practice of demolishing buildings and describes the potential for resource conservation in the construction industry.
 © Angelika Mettke
© Angelika Mettke
The management guide shows concisely what resource efficiency means for a company and how it can benefit from it. A catalog of measures explains the most important starting points that management should address in order to integrate material- and energy-efficient processes into the company.
 © seventyfour/stock.adobe.com
© seventyfour/stock.adobe.com
The VDI ZRE develops instruments that help enterprises implement measures for higher resource effciency. It was launched in 2009 as a cooperative project of the former Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conversation and Nuclear Safety (BMU) and the VDI. As the competence centre for resource effciency, the VDI ZRE works at the interface between business and science and pools know-how gleaned from both theory and practice.
 © www.studioluka.com
© www.studioluka.com
You got questions or need further information?
We look forward to hearing from you! Feel free to get in touch with your request or suggestion.